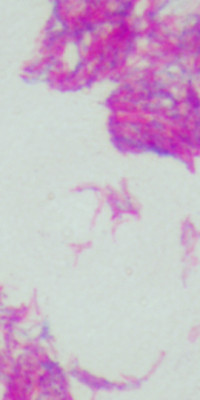
Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis) is a slow-growing aerobic bacterium and the causative agent of tuberculosis in cattle (known as bovine TB). It is related to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium which causes tuberculosis in humans. M. bovis, and can jump the species barrier and cause tuberculosis in humans and other mammals.
Transmission:
Tuberculosis (TB) transmission has been documented in health care settings where health care workers and patients come in contact with people who have TB disease. The disease can be transmitted in several ways; for example, it can be spread in exhaled air, sputum, urine, feces, and pus, so the disease can be transmitted by direct contact, contact with the excreta of an infected animal, or inhalation of aerosols, depending on the species involved.
Symptoms:
Not all M. bovis infections progress to TB disease, so there might be no symptoms at all. If untreated, a person can die of the disease. These include:
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Cough
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea