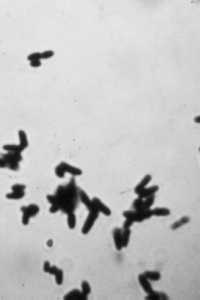
Q: What is C. Bovis?
A: Corynebacterium bovis (C. bovis) is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming bacterium commonly encountered in athymic nude mouse colonies at academic and industry vivaria. This pathogen poses a significant challenge to the research community due to its persistence and resistance to eradication efforts.
Q: How does C. Bovis affect research labs?
A: C. bovis can have a significant impact on research labs, particularly those working with immunocompromised lab animal species. Infections can cause diarrhea, weight loss, reduced fertility, and even death in affected animals. In addition to the direct impact on lab animal health, C. bovis outbreaks can also lead to project delays, additional costs for treatment and decontamination, and potential negative impacts on research data.
Q: Why is it important to prevent and eradicate C. Bovis?
A: Preventing and eradicating C. Bovis is crucial for maintaining the health of lab animal populations and ensuring the integrity of research data. Outbreaks can have serious consequences for animal welfare, scientific progress, and financial resources. By implementing best practices for facility hygiene, using disinfectants with C. bovis label claims, and following established protocols for decontamination, researchers and facility managers can help prevent the spread of C. bovis and protect lab animal health.
Q: How Can I Start a C. Bovis decontamination or C. Bovis remediation?
A: QuipDecon Services by Quip Labs can play a critical role in eradicating C. Bovis from research labs or vivariums. QuipDecon Services are comprised of multiple components that include Quip Laboratories’ proprietary chemistries, state-of-the-art equipment and proven methodologies can help make C. Bovis remediation simple. As industry leaders in biosafety and facility hygiene, we can even provide guidance for design, monitoring, testing and education of both facility staff and researchers.
Working with an industry leader like Quip Labs can ensure that there’s very little operational interruption, and that all proper decontamination and verification steps are taken to eliminate the risks to research that C. Bovis poses.