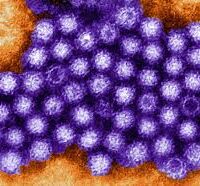
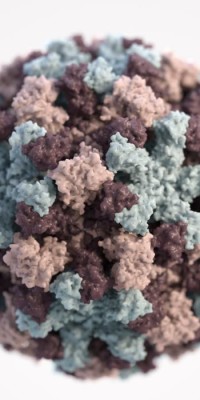
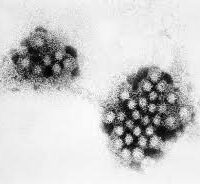
The common “stomach bug”, known as the norovirus, is a highly contagious diarrheal and vomiting bug. The virus thrives in compact populations such as schools, nursing homes, child care centers, cruise ships, and hospitals, commonly spread through food or water that is contaminated during preparation or contaminated surfaces.
Transmission:
Noroviruses are highly contagious and are shed in the feces of infected humans and animals. The virus enters the body through the mouth or eyes through eating contaminated food, drinking contaminated water, or simply being in close contact with a person who is infected with norovirus. Raw or undercooked oysters and raw fruits and vegetables have been implicated in some outbreaks.
Symptoms:
Symptoms typically begin 12 to 48 hours after exposure. Norovirus symptoms last one to three days, and most people recover completely without treatment. These symptoms may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain or cramps
- Watery or loose diarrhea
- Malaise
- Low-grade fever
- Muscle pain