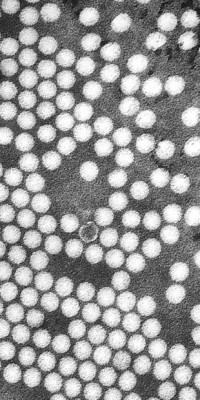
Theilovirus is a non-enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus. Theilovirus, also known as Mouse encephalomyelitis virus, infects the brain and spinal chord of mice and other murines. Infection is most commonly encountered in research facilities due to the virus’s utility as a useful model for multiple sclerosis.
Transmission:
The virus is spread horizontally by contact with feces and urine. Dirty bedding and tight living quarters, such as in research facilities are at the highest risk of transmitting pathogens from infected mice.
Symptoms:
Most infected mice do not express clinical signs of disease once infected. However, a chronic theilovirus infection can result in chronic demyelination of neurons, which is a valuable model in the research of multiple sclerosis. Other symptoms can include:
- Acute encephalitis
- Paralysis
- Neuronal degradation