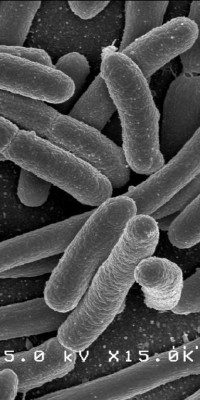
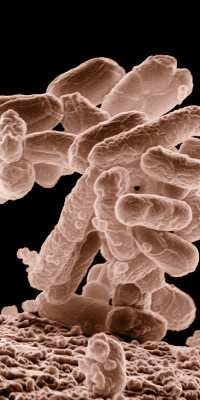
Escherichia coli O157:H7 is a common cause of foodborne illness. Infection often leads to bloody diarrhea, and occasionally to kidney failure. Most illness has been associated with eating undercooked, contaminated ground beef. Person-to-person contact in families and child care centers is also an important mode of transmission. Infection can also occur after drinking raw milk and after swimming in or drinking sewage-contaminated water.
Transmission:
Transmission is via the fecal-oral route, and most illness has been through the distribution of contaminated raw leafy green vegetables, undercooked meat, and raw milk. Swimming in or drinking sewage-contaminated water can also cause infection. Bacteria in diarrheal stools of infected persons can be passed from one person to another if hygiene or handwashing habits are inadequate.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of A. baumannii infections are often indistinguishable from other opportunistic infections caused by other opportunistic bacteria – including Klebsiella pneumoniae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. These include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Malaise
- Loss of appetite
- Dehydration