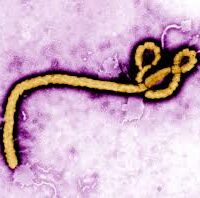
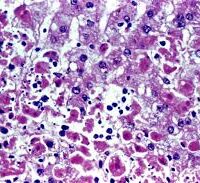
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of viruses that cause a severe multisystem syndrome, failure across multiple organ systems. Characteristically, the overall vascular system is damaged, and the body’s ability to regulate itself is impaired. While some types of hemorrhagic fever viruses can cause relatively mild illnesses, many of these viruses cause severe, life-threatening disease.
Transmission:
The majority of these outbreaks occur with patient-to-patient transmission. However there is a risk of occupational transmission of A. baumannii from a patient to a health care worker (HCW).
Infected patients spread Acinetobacter to the air of intensive care unit (ICU), which can remain in the air for about four weeks and can infect prospective patients more than three months later.
Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of VHFsmost predominantly include fever and bleeding. Manifestations of VHF often also include:
- Flushing of the face and chest
- Small red or purple spots
- Bleeding
- Swelling caused by edema
- Low blood pressure
- Shock
- Malaise
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea