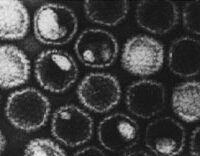
Infectious Laryngotracheitis is a type of herpesvirus affecting the upper respiratory tract of its hosts. The disease is highly infectious and has serious economic implications for poultry and egg production worldwide. Infectious Laryngotracheitis is extremely resistant outside host but is susceptible to disinfectants.
Transmission:
The virus is transmitted primarily through formites of an infected fowl. These particles can become airborne through coughing and sneezing, but also from soiled bedding or unsanitary living conditions. The virus itself has been measured to live in droppings for up to 10 days and in carcasses for up to 70 days after death. As such, it is treated with extreme caution.
Symptoms:
The virus infects the upper respiratory tract of first and clinical signs are most often identified in these areas. Other symptoms may develop to include:
- Nasal discharge
- Coughing and wheezing
- Watery eyes
- Conjunctivitis
- Rales
- Occular discharge